PYTHON EN GRAFICACION
Creacion de un circulo
 from Tkinter import *
from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
circulo = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='black')
circulo.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
circulo.create_oval(10, 10, 200, 200, width=5, fill='red')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de un rectangulo
 basicamente es lo mismo que el circulo
basicamente es lo mismo que el circulo
from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
rectangulo = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
rectangulo.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
rectangulo.create_rectangle(10, 10, 200, 200, width=5, fill='yellow')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de unas lineas
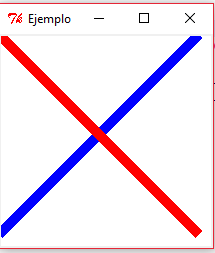
from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
linea = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
linea.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
linea.create_line(0, 200, 200, 0, width=10, fill='blue')
linea.create_line(0, 0, 200, 200, width=10, fill='red')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de una ventana principal
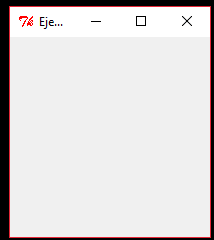
from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ventana')
ventana= Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
root.mainloop()
 from Tkinter import *
from Tkinter import *root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
circulo = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='black')
circulo.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
circulo.create_oval(10, 10, 200, 200, width=5, fill='red')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de un rectangulo
 basicamente es lo mismo que el circulo
basicamente es lo mismo que el circulofrom Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
rectangulo = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
rectangulo.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
rectangulo.create_rectangle(10, 10, 200, 200, width=5, fill='yellow')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de unas lineas

from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ejemplo')
linea = Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
linea.pack(expand=YES, fill=BOTH)
linea.create_line(0, 200, 200, 0, width=10, fill='blue')
linea.create_line(0, 0, 200, 200, width=10, fill='red')
root.mainloop()
Creacion de una ventana principal

from Tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title('Ventana')
ventana= Canvas(width=210, height=210, bg='white')
root.mainloop()
from Tkinter import *
v0 = Tk()
v0.config(bg="red")
v0.geometry("500x500")
v0.mainloop()
Para importar un botón se hace de la siguiente forma:
from Tkinter import *
v0 = Tk()
v0.config(bg="black")
v0.geometry("500x500")
b1=Button(v0,text="ABRIR VENTANA V1")
b1.pack()
v1=Toplevel(v0)
v1.withdraw()
v0.mainloop()
from Tkinter import *
v0 = Tk()
v0.config(bg="black")
v0.geometry("500x500")
b1=Button(v0,text="ABRIR VENTANA V1")
b1.pack()
v1=Toplevel(v0)
v1.withdraw()
v0.mainloop()




Comentarios
Publicar un comentario